Main difference between ethereum and bitcoin explained
Main difference between ethereum and bitcoin is a topic that captivates both novice and seasoned cryptocurrency enthusiasts. As the two leading digital currencies, Bitcoin and Ethereum not only revolutionized the financial landscape but also laid the groundwork for a decentralized future.
Bitcoin, created in 2009, serves primarily as a digital store of value, while Ethereum, introduced in 2015, expanded the concept of blockchain technology by integrating smart contracts, enabling a wide range of applications beyond currency transactions. Understanding their distinctions is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the evolving world of cryptocurrencies.
Overview of Bitcoin and Ethereum

Bitcoin, launched in 2009 by an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto, was the first cryptocurrency and remains the most recognized. It was created as a decentralized digital currency to give people control over their own money without the need for banks or intermediaries. Bitcoin’s primary purpose is to serve as a medium of exchange, allowing peer-to-peer transactions that are secured through blockchain technology.Ethereum, created by Vitalik Buterin and officially launched in 2015, brought forth a revolutionary approach by introducing smart contracts.
Unlike Bitcoin, which focuses solely on transactions, Ethereum aims to be a platform for decentralized applications (dApps) that run on its blockchain. This allows developers to build a wide range of applications, from finance to gaming, utilizing the power of blockchain technology.Both cryptocurrencies serve distinct purposes in the crypto ecosystem. Bitcoin is primarily used as a store of value and means of exchange, while Ethereum facilitates a broader range of functionalities through its smart contract capabilities.
Technical Differences
When it comes to the underlying technology, Bitcoin and Ethereum differ significantly in their consensus mechanisms, transaction speeds, and programming languages.
- Bitcoin operates on a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, requiring miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. This process can be time-consuming and often results in slower transaction speeds.
- Ethereum also started with PoW but is transitioning to Proof of Stake (PoS) with Ethereum 2.0, which aims to improve transaction speeds and lower costs by allowing validators to confirm transactions based on the number of coins they hold.
- Transaction speeds on Bitcoin average around 7 transactions per second (TPS), while Ethereum can handle approximately 30 TPS. However, with the PoS upgrade, Ethereum aims to significantly increase this capacity.
- In terms of programming languages, Bitcoin’s scripting language is limited in functionality, primarily focusing on transaction verification. In contrast, Ethereum uses Solidity, a robust programming language that enables developers to create complex smart contracts.
Monetary Policies

Bitcoin’s monetary policy is characterized by a fixed supply model, capping the total number of coins at 21 million. This scarcity creates an environment similar to precious metals, which can influence its value over time. The fixed supply model means that as demand increases, the price is likely to rise, making Bitcoin a deflationary asset.On the other hand, Ethereum does not have a fixed supply limit.
Instead, it has a flexible issuance model that allows for new coins to be created, which can lead to inflation. This approach supports network security and incentivizes validators, particularly as Ethereum transitions to PoS.The economic models of Bitcoin and Ethereum reflect their respective purposes: Bitcoin’s fixed supply promotes scarcity and value preservation, while Ethereum’s adaptable issuance allows for ongoing development and enhancement of its platform.
Smart Contract Capabilities
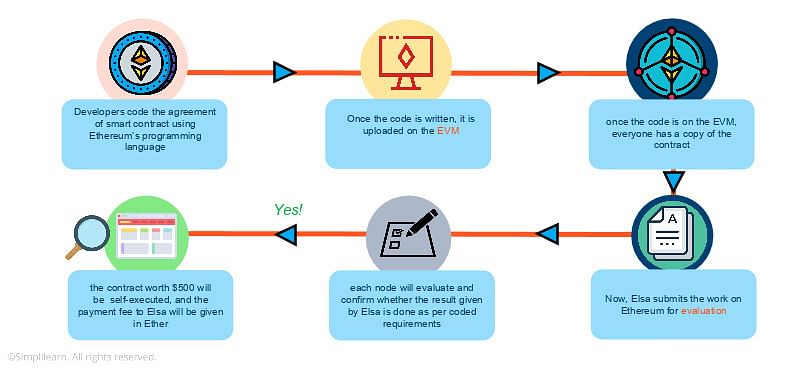
Ethereum’s most significant innovation is its smart contract functionality, which enables self-executing contracts with the rules directly written into code. This allows for automated transactions and operations without intermediaries, streamlining processes across various industries.In contrast, Bitcoin’s scripting capabilities are more limited, focusing primarily on transaction validation without the complex conditions possible in Ethereum. While Bitcoin can implement basic smart contracts, its functionality pales compared to what Ethereum offers.Examples of applications utilizing Ethereum’s smart contracts include decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, which allow users to lend, borrow, and trade without traditional financial institutions, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which represent ownership of unique digital assets.
Network Security and Scalability
Bitcoin’s blockchain is well-known for its security, primarily due to the extensive network of miners that validate transactions. The PoW mechanism, while energy-intensive, has proven effective in protecting the network from attacks.Ethereum is currently enhancing its security features through the transition to Proof of Stake. This shift is expected to not only improve energy efficiency but also bolster security by reducing the chances of centralization among validators.Both cryptocurrencies are actively pursuing scalability solutions.
Bitcoin is exploring technologies like the Lightning Network, which facilitates faster off-chain transactions. Meanwhile, Ethereum’s transition to sharding aims to allow multiple transactions to be processed simultaneously, significantly increasing its throughput.
Community and Ecosystem
The Bitcoin community is supported by various key players, including developers, miners, and advocates dedicated to its vision of financial independence and decentralization. Influential figures, such as Andreas Antonopoulos, have contributed significantly to educational efforts surrounding Bitcoin.Ethereum, conversely, has nurtured a vibrant ecosystem that encompasses a wide range of applications beyond simple transactions. DeFi projects, NFTs, and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) have all flourished on the Ethereum platform, attracting a diverse community of developers and users.When comparing governance models, Bitcoin relies on a more informal process where decisions are made through community consensus.
Ethereum, however, has developed a more structured approach with improvement proposals (EIPs) that allow stakeholders to discuss and vote on changes to the protocol.
Market Position and Adoption
As of late 2023, Bitcoin remains the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, valued at over $400 billion, while Ethereum follows closely with a market cap of around $200 billion. The trading volume for both cryptocurrencies can fluctuate widely, reflecting market sentiment and adoption levels.Adoption rates for Bitcoin and Ethereum vary across different sectors. Bitcoin is often seen as a digital gold and is increasingly accepted by retailers and institutional investors.
Ethereum’s adoption is driven by the growing interest in DeFi and NFTs, with numerous platforms integrating its technology into their services.Public perception also differs, with Bitcoin often portrayed as a revolutionary financial tool, while Ethereum is recognized for its technological advancements and applications. Media coverage tends to highlight Bitcoin’s price movements, whereas Ethereum’s developments in smart contracts and dApps receive significant attention.
Future Outlook
The future of Bitcoin looks toward solidifying its role as a store of value and medium of exchange. Potential developments include enhanced privacy features and greater institutional adoption, which could drive demand and price stability.Ethereum’s roadmap includes upgrades focused on scalability and security, particularly with the continued rollout of Ethereum 2.0. Upcoming features such as sharding and improved transaction speeds are anticipated to strengthen its position as the leading platform for decentralized applications.Both cryptocurrencies face challenges ahead, including regulatory scrutiny and competition from emerging blockchain technologies.
Navigating these hurdles will be crucial for their sustained growth and acceptance in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Epilogue

In summary, the main difference between ethereum and bitcoin highlights their unique functionalities, ecosystems, and future prospects. While Bitcoin remains a digital gold, Ethereum’s versatility opens new avenues for innovation and decentralized applications. As both cryptocurrencies continue to evolve, staying informed about their differences can be key to making informed investment decisions.
Detailed FAQs
What is the main use of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is primarily used as a digital store of value and a medium of exchange.
What advantages does Ethereum offer over Bitcoin?
Ethereum allows for smart contracts and decentralized applications, providing more versatility than Bitcoin.
How does Bitcoin’s supply model differ from Ethereum’s?
Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins, while Ethereum does not have a capped supply and follows a different issuance model.
What are gas fees in Ethereum?
Gas fees are transaction fees paid to miners for processing transactions and executing smart contracts on the Ethereum network.
Is Bitcoin or Ethereum more widely adopted?
Bitcoin is often seen as more widely adopted as a digital currency, while Ethereum is leading in decentralized finance and NFTs.