Ethereum Smart Contracts Explained A Comprehensive Guide
ethereum smart contracts explained sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, operating on the Ethereum blockchain. They revolutionize the way agreements are made, eliminating the need for intermediaries and ensuring transparency and security in transactions. With their ability to automate processes and execute contracts once predetermined conditions are met, Ethereum smart contracts have become a cornerstone of modern decentralized applications.
Introduction to Ethereum Smart Contracts
Ethereum smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into code. They are a vital component of the Ethereum blockchain, enabling decentralized applications (dApps) to function without the need for intermediaries. Their significance lies in their ability to automate processes and enforce agreements transparently and securely.Unlike traditional contracts, which often require third parties for enforcement, Ethereum smart contracts operate on a decentralized network.
This means they are immutable, meaning once deployed, the code cannot be altered, and they can execute automatically when conditions are met. The technology powering these contracts is blockchain, which ensures that all transactions are recorded securely and are publicly verifiable.
Mechanism of Ethereum Smart Contracts
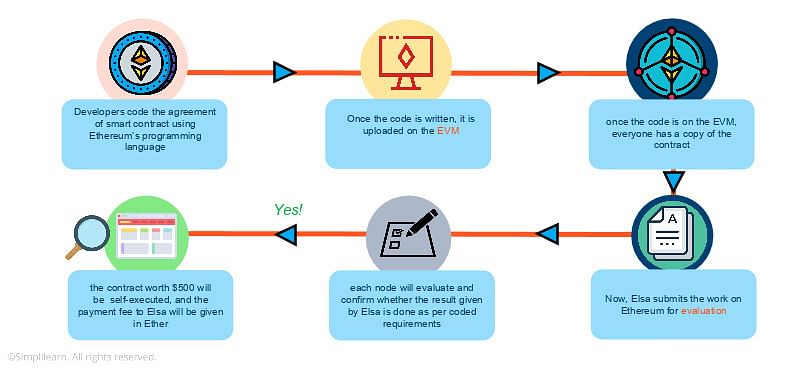
Creating and deploying Ethereum smart contracts involves a systematic approach. Developers write smart contracts using a programming language called Solidity, which is tailored for Ethereum. After writing the code, it is compiled and deployed onto the Ethereum blockchain. The Ethereum network then validates and executes the contract.The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) plays a crucial role in executing these smart contracts.
It acts as a runtime environment, ensuring that the contracts operate correctly on the network. Every operation executed in the EVM incurs gas fees, which are necessary for processing transactions and incentivizing miners to validate them. Gas fees vary based on network demand and the complexity of the operations.
Use Cases of Ethereum Smart Contracts

Ethereum smart contracts have found applications across various industries, revolutionizing traditional operations. Some of the prominent sectors utilizing these contracts include:
- Finance: Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms use smart contracts for lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries.
- Real Estate: Smart contracts facilitate transparent property transactions, handling everything from escrow to ownership transfer.
- Supply Chain: Companies employ smart contracts to track products, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud.
- Gaming: In-game assets can be tokenized and traded securely on blockchain platforms, enhancing user ownership and engagement.
Successful projects like Uniswap in DeFi and Cryptokitties in gaming illustrate the potential of Ethereum smart contracts. These use cases deliver benefits such as increased efficiency, reduced costs, and heightened security, making business operations smoother for both enterprises and individuals.
Security Considerations
Despite their advantages, Ethereum smart contracts are not immune to vulnerabilities. Common security issues include reentrancy attacks, overflow/underflow problems, and improper access control. Developers must be vigilant about such vulnerabilities when coding their contracts.Best practices for ensuring the security of smart contracts include regular audits, using established security patterns, and testing thoroughly before deployment. For example, the notorious DAO hack in 2016 highlighted the importance of rigorous testing and auditing, as it led to significant financial losses and prompted discussions about governance in the Ethereum ecosystem.
Future of Ethereum Smart Contracts

The future of Ethereum smart contracts is bright, with ongoing advancements in technology. Potential improvements include enhanced scalability solutions like Layer 2 protocols, which aim to reduce congestion on the Ethereum mainnet and lower transaction fees. These advancements will enable more complex dApps to operate efficiently.Regulatory developments are another factor that will shape the future landscape of smart contracts. As governments begin to recognize and regulate blockchain technologies, smart contracts may evolve to meet compliance requirements, potentially increasing their adoption in mainstream sectors.
Creating Your Own Ethereum Smart Contract
Writing a basic Ethereum smart contract using Solidity is an accessible process for developers. The following steps Artikel the key stages:
- Set Up Your Environment: Install necessary tools such as Node.js, Truffle, and Ganache.
- Write the Contract: Create your smart contract code using Solidity.
- Compile the Contract: Use the Solidity compiler to convert your code into bytecode.
- Deploy the Contract: Deploy the compiled contract to the Ethereum blockchain using a wallet like MetaMask.
- Test the Contract: Use frameworks like Truffle or Hardhat to test your contract for bugs and ensure functionality.
Developers can utilize various tools and platforms such as Remix for coding, and Infura for connecting to the Ethereum network. Optimizing smart contracts for performance and cost-efficiency involves minimizing gas usage by reducing complexity and avoiding expensive operations, ensuring that the contracts run smoothly and economically.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the exploration of Ethereum smart contracts unveils a transformative technology that reshapes industries and empowers individuals. As we move forward, understanding their mechanisms, potential applications, and security considerations is crucial. The future looks promising, as advancements in technology and regulations continue to evolve, paving the way for wider adoption and innovative solutions.
FAQ Resource
What are the main advantages of using Ethereum smart contracts?
They offer automation, transparency, security, and reduced costs by eliminating intermediaries.
How do smart contracts ensure security?
Smart contracts use cryptographic algorithms and are executed on a decentralized network, making manipulation difficult.
Can smart contracts be modified after deployment?
Generally, they cannot be modified; however, developers can create upgradeable contracts with certain design patterns.
What programming language is primarily used to write Ethereum smart contracts?
Smart contracts on Ethereum are primarily written in Solidity.
What is the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)?
The EVM is a decentralized computing environment that executes smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.